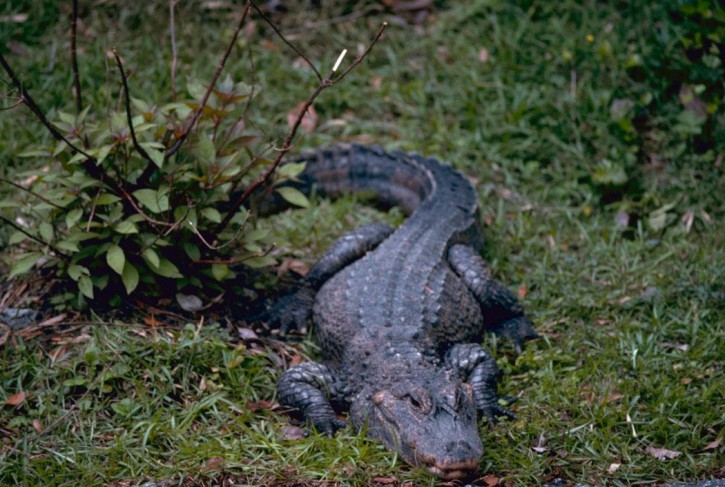
The Chinese Alligator is one of the rarest crocodilian and the smallest of the only two alligator species surviving today. It is also known as Yangtze Alligator as it it found only the Yangtze river system of China.
The Scientific Name : Alligator sinensis
Where is it found?
Once the Chinese alligator was found in the extensive lakes and marshlands of the middle-lower Yangtse River region and along the river from Shanghai to Jianling City. Due to its rarity and also secretive behavior, in recent historical times the alligator have never been abundant. Due to rapid habitat loss and uncontrolled killing of the species with the human population growth in China, the Chinese alligator was found only in scattered groups in southeastern Anhui Province and parts of adjacent Zhejiang and Jiangau provinces as early as 1920s. Today the alligator species is mostly restricted to a 433 square kilometer reserve in the Anhui province of the lower Yangtze. Chinese alligators prefers slow-moving freshwater sources including marshlands, ponds, lakes, reservoirs and river backwater canals. With the loss of natural habitats, they are also found in rice paddies, irrigation networks, etc in recent times.
How does it live?
The Chinese alligator is an opportunistic feeder. Its diet mostly includes snails, crustaceans, insects and fish, but young waterfowl and rodents are also taken if available. They are not known to have eaten any large mammals. In recent days are known to have attacked ducks of the villagers, for which it has faced the wrath of human society quite often. The alligators spend most of their lifetime in burrows avoiding extreme winters and also human intervention during daylights. They hunt only during the summer from April to October during nights. They reach adulthood at an age of 4-5 years. The mating is polygamous and usually very aggressive when the opposite sexes meet. The breeding period is the summer and the female lays 10-15 eggs. The incubation period is usually around 70 days. Social life of the Chinese alligator starts during the incubation period only, when nest mates communicate egg to egg and with parents who open the egg chamber. This results in synchronized hatching. The babies spend weeks to years under the protection of the mother. Juvenile makes a vocal sound to bring the group together , and mother also respond to then with a distress call. Chinese Alligator known to have a lifespan of around 50 years in wild and 70 years in captivity.
How does it look?
Chinese Alligator is considered to be one of the smallest crocodilian species. It normally reaches 5 feet in length. The largest alligator measured in recent times was 7 feet 1 inch. It can barely weigh upto 45 kg. Whole body of the Chinese alligator is covered with dar green abd black scales. The scales are harder on back and softer on the sides and belly. Even the upper lids are covered with boney scales for this alligator which is a major difference with it’s other counterpart, the American Alligator. The Chinese alligator has 72-76 teeth, adapted more for crushing shells of molluscs. The juveniles are black with bright yellow cross-banding.
What are the threats?
Habitat loss is cited as the most important threat for the Chinese Alligators. Most of the natural wetlands, marshlands were destroyed in the past decades for agriculture and other developments. Building dams in the river system have eliminated core habitats of the alligator. The remaining natural habitats are also frequently destroyed by flooding of the Yangtse river.
Apart from habitat loss, human-alligator conflict has killed many of the precious species in the past. Though the alligator is not capable of attacking or killing large mammals or humans, the very concept of considering any crocodilian species as dangerous predator in culture has killed many innocent animals. Also the large burrow created by the alligators hamper the irrigation system of the farmers at times, which make the farmers angry towards the species.
Many of the Chinese alligators have been killed due to their meat value in the Chinese market. There is a mythical believe that the alligator’s meat can cure many diseases including cancer. Any human-alligator conflict which always results in the killing of the alligator, usually ends in the market of China selling meat and various other organs of the alligator by the farmers.
Conservation Efforts
Some experts considered the Chinese Alligator as extinct evern during 1920s. But later some fragmented populations were discovered in wild. There was no significant research or conservation effort held on the species till the Communist revolution in China in 1949. The need of protection of alligator became important only post revolution stage. In 1972 for the first time Chinese government listed Chinese Alligator as the first class endangered animal of the country. In 1979, captive breeding centers were established in Anhui and Zhejiang provinces. The government conservation efforts has been more focused on the captive population rather than the wild survivors. Almost till date, the wild eggs are collected artificially incubated to increase the captive population. The first ever scientific study on the alligator was done in 1980 with the collaboration of both Chinese and US scientists. The studies were performed in the captive breeding centers and all the knowledge on the Chinese alligator in till recent times are based on these studies. In 1990s the species got international recognition as critically endangered species. In recent days public awareness has also been created to reduce any killing of the species in the wild. The captive breeding centers releases live alligators for the meat business to counter the market demands and also recover their costs. In last couple of years there have been reports of the species recovering in the wild, with the population stregth growing from 100 to 300. The captive breeding programs have been largely successful with a population strength of whooping 10000 now. The conservationists are now concentrating on reintroducing the alligators into wild from the captive centers. Some of the organizations that work for the conservation of the species now are Wildlife Conservation Society, Department of Wildlife Conservation and Management of the State Forestry Administration of China,
The Chinese Alligator – Species on the Brink





Recent Comments